The django-import-export library supports multiple formats, including xls, csv, json, yaml, and all other formats supported by tablib. It also have a Django admin integration, which is really convenient to use.
Installation & Configuration
Let’s build a project to understand it better. Create a new Django project named dashboard and inside it create a new app named reports.
To install the package, run the following command:
pip install django-import-export
Then, in your settings.py add your app name (reports) and import-export library into INSTALLED_APPS:
INSTALLED_APPS = (
...
'import_export',
'reports'
)
I also recommend to add optional configuration to end of settings.py:
IMPORT_EXPORT_USE_TRANSACTIONS = True
The default value is False. It determines if the library will use database transactions on data import.
After this section I will show you main parts of the project. If you don't know how to configure urls.py or templates, I will put GitHub repo link end of this post, so you can clone and run the project.
Create Model and Resources
In your models.py create a model named Employee:
from django.db import models
class Employee(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=30)
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=60)
email = models.EmailField(blank=True)
day_started = models.DateField()
location = models.CharField(max_length=100, blank=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.first_name
The django-import-export library works with the concept of Resource, which is class definition very similar to how Django handles model forms and admin classes.
If you want to handle data directly from Django admin then you should put the code inside the admin.py file.
However, our implementation for this project is not related to the Django admin, so let's create resources.py file inside app folder.
from import_export import resources
from .models import Employee
class EmployeeResource(resources.ModelResource):
class Meta:
model = Employee
Export Data
Well, we are going to create form and let the user to select format of file. Update your views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.http import HttpResponse
from tablib import Dataset
from .resources import EmployeeResource
from .models import Employee
def export_data(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
# Get selected option from form
file_format = request.POST['file-format']
employee_resource = EmployeeResource()
dataset = employee_resource.export()
if file_format == 'CSV':
response = HttpResponse(dataset.csv, content_type='text/csv')
response['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="exported_data.csv"'
return response
elif file_format == 'JSON':
response = HttpResponse(dataset.json, content_type='application/json')
response['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="exported_data.json"'
return response
elif file_format == 'XLS (Excel)':
response = HttpResponse(dataset.xls, content_type='application/vnd.ms-excel')
response['Content-Disposition'] = 'attachment; filename="exported_data.xls"'
return response
return render(request, 'export.html')
It is very simple, when user selects JSON, file will exported as JSON or if user selects CSV then file will exported as CSV.
export.html
Import Data
Assume that we have file named employees.csv:
first_name,last_name,email,day_started,location,id
Peter,Parker,[email protected],2015-05-18,New York,
James,Bond,[email protected],2014-08-11,London,
The id must be present because it is the primary key. It will be generated automatically.
So, we need to import CSV or JSON file to database. Add following function to your views.py:
def import_data(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
file_format = request.POST['file-format']
employee_resource = EmployeeResource()
dataset = Dataset()
new_employees = request.FILES['importData']
if file_format == 'CSV':
imported_data = dataset.load(new_employees.read().decode('utf-8'),format='csv')
result = employee_resource.import_data(dataset, dry_run=True)
elif file_format == 'JSON':
imported_data = dataset.load(new_employees.read().decode('utf-8'),format='json')
# Testing data import
result = employee_resource.import_data(dataset, dry_run=True)
if not result.has_errors():
# Import now
employee_resource.import_data(dataset, dry_run=False)
return render(request, 'import.html')
Let the user to select format of file which will imported.
import.html
Once you imported your file go and check admin and you will see imported data in your model.
Django Admin
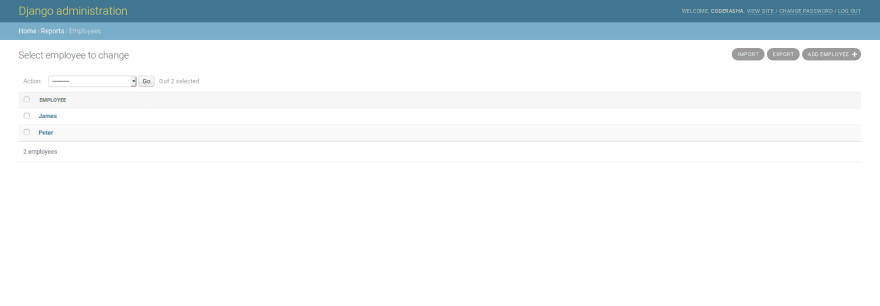
If you want to use import export in admin then simply add following code in your admin.py:
from import_export.admin import ImportExportModelAdmin
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Employee
@admin.register(Employee)
class EmployeeAdmin(ImportExportModelAdmin):
pass
Here's how it looks like: